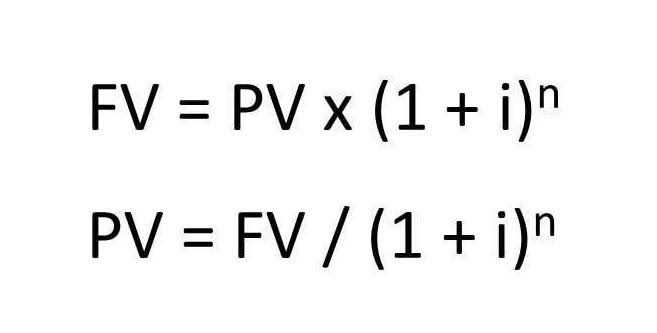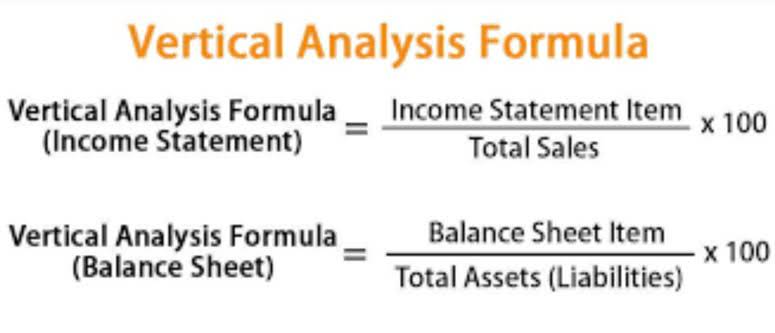
The percentage difference may not be that great, but there’s a chance the “free float” of shares may affect stock prices and raise some modest concerns. Stock dividends don’t affect a company’s cash reserves one way or the other. On the balance sheet, they affect the shareholders’ equity column. Regardless of whether a dividend is paid in cash or stock, dividends reduce a company’s share price by an equivalent amount to the dividend that is paid. The importance of tax-efficient investing with dividends is huge. You have to think about immediate taxes versus taxes you can delay.
Big Tech Q4 Earnings and the Future of the Magnificent 7 Stocks
This performance underscores the company’s strategic focus on high-demand areas. Additionally, CFO David Schulz highlighted the generation of $280 million in free cash flow, representing 145% of adjusted net income, which showcases effective financial management. The company’s ability to consistently outperform market averages since mid-2021 further emphasizes its competitive edge.
- On the balance sheet, they affect the shareholders’ equity column.
- When a company issues stock dividends, it can increase shareholder value.
- More investors may decide to buy shares, improving the company’s image in the market.
- Thus the management or the board of directors have to decide whether the business will pay cash or stock dividend to the investors and the decision depends on many factors.
- If ABC has 1 million shares of stock outstanding, it must pay out $1.5 million in dividends.
Key Assets Propelling WESCO International Forward
The message is that it’s making enough cash to give some back directly to shareholders. When dividends are actually paid to shareholders, the $1.5 million is deducted from the dividends payable subsection to account for the reduction in the company’s liabilities. The cash sub-account of the assets section is also reduced by $1.5 million.
Stock Dividend vs Cash Dividend: Understanding the Key Differences for Investors

With a stock dividend, you get a stock equivalent to a given amount of money. A cash dividend may raise concerns that the company’s forward momentum has halted. After they’re paid, the dividend payable is switched around and is no longer a liability. But the effect is a decrease in the company’s retained earnings, which is one reason the share price goes down. Here are a few of the main points of comparison in the discussion of cash dividends vs. stock dividends.

- In many areas, dividends are taxed at a higher rate than long-term capital gains.
- Meanwhile, global share buybacks are headed towards their lowest level since 2020.
- This transfers economic value from the company to the shareholders instead of the company using the money for operations.
- Cash dividends occur when companies pay shareholders a portion of their earnings in cash.
- Engel also pointed out the potential impacts of the upcoming U.S. election, which could influence investment priorities and market dynamics.
- Companies can retain cash for reinvestment and improve liquidity.
But if you earned stock dividends that equaled $300 in current value, that price isn’t going to be the same tomorrow. Hopefully, after a modest dip in share price, it’s going to appreciate as the company grows. If you hang on to that stock, it’s going to be worth more than $300 in the future. The money the company gives out as cash dividends doesn’t go toward those efforts. One upshot of cash dividends is that they generally have a temporary downward effect on the company’s share price. After a dividend is paid out, you’ll probably see the share value go down by roughly the amount of the dividend.
Chart showing Apple’s share buybacks
In fluctuating market conditions, dividends can offer a sense of stability by delivering reliable returns despite changes to stock prices. Cash dividends are issued by companies because they both cash dividends and stock dividends already obtained ample earnings. It is predicted that giving back to their shareholders will not affect long-term financial strength. These cash-dividend paying companies pay out cash because they might have a good financial position but has a limited capability to venture on expansion to spend their cash up.
- The shareholder that owns 10% from the shareholder’s equity will maintain its portion from it after earning a 20% stock dividend and the market price of the stock remains the same.
- Let’s say 10% is issued as a dividend on a $200 par value per share.
- Large stock dividends occur when the new shares issued are more than 25% of the value of the total shares outstanding before the dividend.
- When deciding how to pay dividends, companies look at several important factors.
- It’s not something you can quantify, but it is something that long-term shareholders seem to value.
As companies consider stock dividends as a way to address liquidity issues during the COVID-19 environment, investors should keep these differences in mind. The amount of cash dividend that investors will periodically acquire depends Bookstime on how many times the company will issue annually. Using the previous example, the company pays cash dividends quarterly.
Key Takeaways

For example, Union Pacific Corp. (UNP) pays a dividend of $3.88 per year per share. The $150 share price means that the dividend represents a 2.55% dividend yield—a metric that can be easily compared between companies. Dividends signal that a company has stable cash flow and is generating profits. A company with a long history of dividend payments that declares a reduction or elimination of its dividend signals trouble. AT&T Inc. cut its annual dividend in half to $1.11 on Feb. 1, 2022, and its shares fell 4% that day.

The company’s strong financial management, evidenced by generating $280 million in free cash flow, supports its ability to reward shareholders and invest in future growth. However, challenges in the utility and broadband segments necessitate strategic adjustments to unlock potential petty cash growth. Navigating economic and regulatory challenges effectively will be essential for sustaining its market position and ensuring continued success. Large stock dividends occur when the new shares issued are more than 25% of the value of the total shares outstanding before the dividend. In this case, the journal entry transfers the par value of the issued shares from retained earnings to paid-in capital.